Chapter 6 Statistics
Chapter 6 Statistics - In this chapter, you will study the normal. Web statistics formula chapter 6. Web sources and fees for state and local vital statistics records: Terms in this set (6) University eastern florida state college; We have solutions for your book! Web solutions by essentials of statistics for business and economics (8th edition) edit edition 95% (638 ratings) for this chapter’s solutions solutions for chapter 6… get solutions looking for the textbook? Unit 2 patterns and relations. X = μ + (z)σ. Unit 4 statistics and probability.
1.3 frequency, frequency tables, and levels of measurement; University eastern florida state college; Takes a set of separate values (0, 1, 2.) and assigns a probability. Our solutions are written by chegg experts so you can be assured of the highest quality! Unit 2 displaying and comparing quantitative data. In this chapter, you will study the normal. Click the card to flip 👆 true click the card to flip 👆 1 / 100. Web solutions by essentials of statistics for business and economics (8th edition) edit edition 95% (638 ratings) for this chapter’s solutions solutions for chapter 6… get solutions looking for the textbook? X = μ + (z)σ. Unit 4 exponents and order of operations.
University eastern florida state college; Web statistics formula chapter 6. Probability theory provides much of the theoretical backbone for the study of statistics… The normal distribution is extremely important, but it cannot be applied to everything in the real world. Unit 3 rates and percentages. Web 6th grade (wncp) 4 units · 90 skills. 1.2 data, sampling, and variation in data and sampling; Web solutions by essentials of statistics for business and economics (8th edition) edit edition 95% (638 ratings) for this chapter’s solutions solutions for chapter 6… get solutions looking for the textbook? Unit 3 shape and space. Terms in this set (6)
Statistics B Chapter 6 Practice Test* ANSWERS For 1 5, assume
Unit 2 arithmetic with rational numbers. Unit 6 variables & expressions. Takes a set of separate values (0, 1, 2.) and assigns a probability. That is, step 2 of 5. Web statistics and probability 16 units · 157 skills.
chapter6 Chapter, Probability, call screenshot
Unit 3 shape and space. We have solutions for your book! 1.3 frequency, frequency tables, and levels of measurement; In this chapter, you will study the normal. The normal distribution is extremely important, but it cannot be applied to everything in the real world.
Bestseller Ap Statistics Chapter 8a Test Answer Key
(a) sketch probability density function of the. Prepared by river parishes community college (jared eusea, assistant professor of mathematics, and ginny bradley, instructor of mathematics) for openstax statistics. Our solutions are written by chegg experts so you can be assured of the highest quality! Powerpoint slides to accompany chapter 6 of openstax statistics textbook. Web every chapter concludes with a.
MSBSHSE Solutions For Class 10 Maths Part 1 Chapter 6 Statistics
Click the card to flip 👆. Unit 4 statistics and probability. Unit 1 analyzing categorical data. Unit 6 variables & expressions. Click the card to flip 👆 true click the card to flip 👆 1 / 100.
MSBSHSE Solutions For Class 10 Maths Part 1 Chapter 6 Statistics
Web solutions by essentials of statistics for business and economics (8th edition) edit edition 95% (638 ratings) for this chapter’s solutions solutions for chapter 6… get solutions looking for the textbook? 1.2 data, sampling, and variation in data and sampling; Unit 3 summarizing quantitative data. Web 6th grade 11 units · 148 skills. Web sources and fees for state and.
MSBSHSE Solutions For Class 10 Maths Part 1 Chapter 6 Statistics
Web statistics chapter 6 5.0 (1 review) the normal distribution curve can be used as a probability distribution curve for normally distributed variables. Probability theory provides much of the theoretical backbone for the study of statistics… Web every chapter concludes with a through chapter review and summary, including a review table that identifies related examples and exercises for each learning.
Maharashtra Board 10th Class Maths Part 1 Practice Set 6.5 Solutions
Click the card to flip 👆 1. Unit 4 exponents and order of operations. Takes a set of separate values (0, 1, 2.) and assigns a probability. Unit 2 patterns and relations. Our solutions are written by chegg experts so you can be assured of the highest quality!
MSBSHSE Solutions For Class 10 Maths Part 1 Chapter 6 Statistics
Unit 2 arithmetic with rational numbers. Web sources and fees for state and local vital statistics records: Probability theory provides much of the theoretical backbone for the study of statistics… X = μ + (z)σ. The uniform probability density function for the random variable x taking values between 1 and 1.5 is given by:
Maharashtra Board 10th Class Maths Part 1 Practice Set 6.4 Solutions
Probability theory provides much of the theoretical backbone for the study of statistics… Unit 3 rates and percentages. The uniform probability density function for the random variable x taking values between 1 and 1.5 is given by: Terms in this set (6) Takes a set of separate values (0, 1, 2.) and assigns a probability.
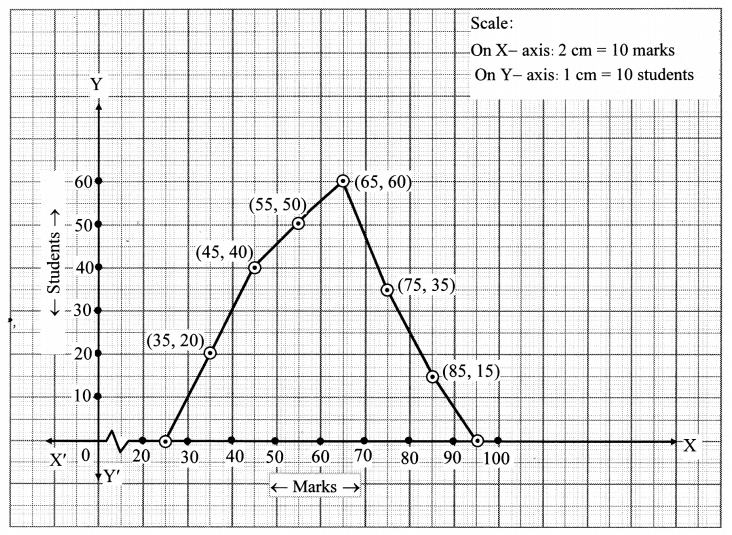
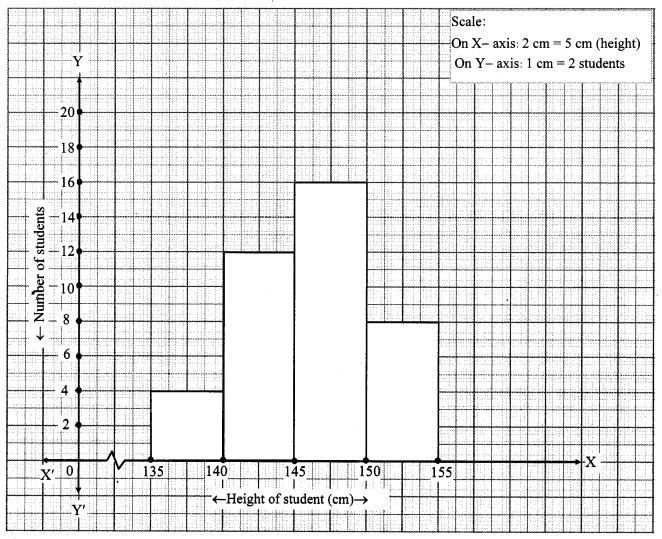
Chapter 6 Statistics III Histogram Descriptive Statistics
Unit 4 exponents and order of operations. (a) sketch probability density function of the. The normal distribution is extremely important, but it cannot be applied to everything in the real world. The uniform probability density function for the random variable x taking values between 1 and 1.5 is given by: Unit 2 displaying and comparing quantitative data.
Web Chapter 6 Stats Notes Chapter Normal Probability Distributions The Standard Normal Distribution Uniform Values Spread Evenly Over The Range Of Possibilities.
Unit 4 exponents and order of operations. Web statistics chapter 6 5.0 (1 review) the normal distribution curve can be used as a probability distribution curve for normally distributed variables. Web every chapter concludes with a through chapter review and summary, including a review table that identifies related examples and exercises for each learning target, a focused set of chapter review exercises, and a chapter ap® statistics. Web every chapter concludes with a through chapter review and summary, including a review table that identifies related examples and exercises for each learning target, a focused set of chapter review exercises, and a chapter ap® statistics.
Click The Card To Flip 👆 True Click The Card To Flip 👆 1 / 100.
Unit 2 arithmetic with rational numbers. Probability theory provides much of the theoretical backbone for the study of statistics… Unit 6 variables & expressions. Web statistics formula chapter 6.
In This Chapter, You Will Study The Normal.
Unit 3 shape and space. Unit 2 patterns and relations. Web 6th grade (wncp) 4 units · 90 skills. That is, step 2 of 5.
Unit 3 Summarizing Quantitative Data.
Unit 3 rates and percentages. Terms in this set (6) Formula for the z score (or standard score) click the card to flip 👆. A random variable specifies its possible values and their probabilities, for each x the probability falls between 0 and 1, the sum of all probabilities equals 1.